Palace of Culture and Science
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The Palace of Culture and Science (PKiN), is a modernist high-rise building in Warsaw, Poland. At 237 m (778 ft) tall, including a 43 m-high spire, it is the tallest building in Poland, and one of the most visible and recognisable landmarks in Warsaw.
Completed in 1955, PKiN has long provoked controversy as it was intended as a ‘gift’ from the Soviet Union to Poland, but many considered it to be a symbol of Soviet domination; indeed its original name was the Joseph Stalin Palace of Culture and Science.
The negativity felt by Poles towards the building was also due to the design following that of the ‘Seven Sisters’ high-rises in Moscow, leading to many seeing the PKiN as an ‘oppressive outpost’ of the USSR in the centre of Warsaw. Indeed, it is often referred to as the ‘Eighth Sister’. Stalin’s name was removed from the building in the wake of the ‘De-Stalinisation’ process that took place after the leader’s death through to Polish independence in the early-1990s.
Today, the PKiN has gained more acceptance among Poles, particularly younger generations. The urbanist writer Owen Hatherley praised the building, describing it as architecturally superior to the ‘Seven Sisters’ upon which it was modelled.
[edit] Design and construction
The main architect for the building was Lev Rudnev, who followed the architecture of the ‘Seven Sisters’ high-rises in Moscow, which are often likened to shorter and more squat versions of the American art deco skyscrapers such as the Empire State Building. Rudnev attempted to create an eclectic mix of a steel-framed structure with Russian baroque and gothic details.
However, Rudnev also visited several Polish heritage sites in Krakow and Zamosc to study the Polish Renaissance architecture of the houses and palaces there. As a result, he decorated the roof with spiky masonry ‘Polish parapets’. Regardless of this, many critics at the time and since completion, argued that the monumental scale of the building was at odds with the aesthetic balance of the old city of Warsaw and that it imposed dissonance with its surroundings.
The elaborate exterior is surrounded by monumental classical sculptures of Copernicus, Adam Mickiewicz, Marie Curie, and others. The interior is also very elaborate, with marble floors, vast staircases, gilded finishes and large glass chandeliers.
Construction began in 1952, when most of the surrounding area, and indeed the rest of the city, still lay in ruins after the Second World War. It was built by 3,500-5,000 Russian and 4,000 Polish workers.
[edit] Post-completion
As Poland asserted itself post-Soviet Bloc status, and since gaining membership of the European Union, attitudes towards the PKiN have begun to soften, particularly in the wake of more high-tech, modernist skyscrapers completed in the last few years.
The building serves as headquarters of a number of private companies and public institutions. It hosts concerts, museum exhibitions, a popular cinema, bars and even Poland’s largest casino. The 30th floor terrace provides a panoramic view of the city and is a popular tourist attraction.
In 1999 four clock faces measuring 6.3 m in height were added to the top of the building in time for the celebrations of Millennium Eve.
In 2010, high-power LED lights were installed as a means of modernising the lighting of the buildings and allowing a range of colours to be displayed at night and for special occasions.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Building of the week series.
- Empire State Building.
- Imagine Moscow exhibition.
- Ministry of Transportation Building, Georgia.
- Nowa Huta - Communist tour review.
- Owen Hatherley - Landscapes of Communism.
- Socialist realism in a post-war Czechoslovak new town.
- The Kremlin.
- Upside Down House, Poland.
- Zlota 44, Warsaw.
Featured articles and news
International Women's Day 8 March, 2025
Accelerating Action for For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.
Lack of construction careers advice threatens housing targets
CIOB warning on Government plans to accelerate housebuilding and development.
Shelter from the storm in Ukraine
Ukraine’s architects paving the path to recovery.
BSRIA market intelligence division key appointment
Lisa Wiltshire to lead rapidly growing Market Intelligence division.
A blueprint for construction’s sustainability efforts
Practical steps to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Timber in Construction Roadmap
Ambitious plans from the Government to increase the use of timber in construction.
ECA digital series unveils road to net-zero.
Retrofit and Decarbonisation framework N9 launched
Aligned with LHCPG social value strategy and the Gold Standard.
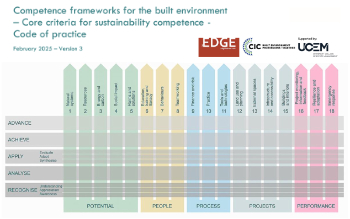
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
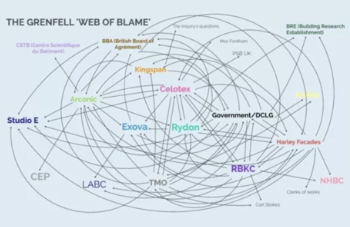
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.
A brief description and background to this new February law.
Everything you need to know about building conservation and the historic environment.
NFCC publishes Industry White Paper on Remediation
Calling for a coordinated approach and cross-departmental Construction Skills Strategy to manage workforce development.
'who blames whom and for what, and there are three reasons for doing that: legal , cultural and moral"